
Users may set up SSH tunnels to transfer unencrypted traffic over a network through an encrypted channel.
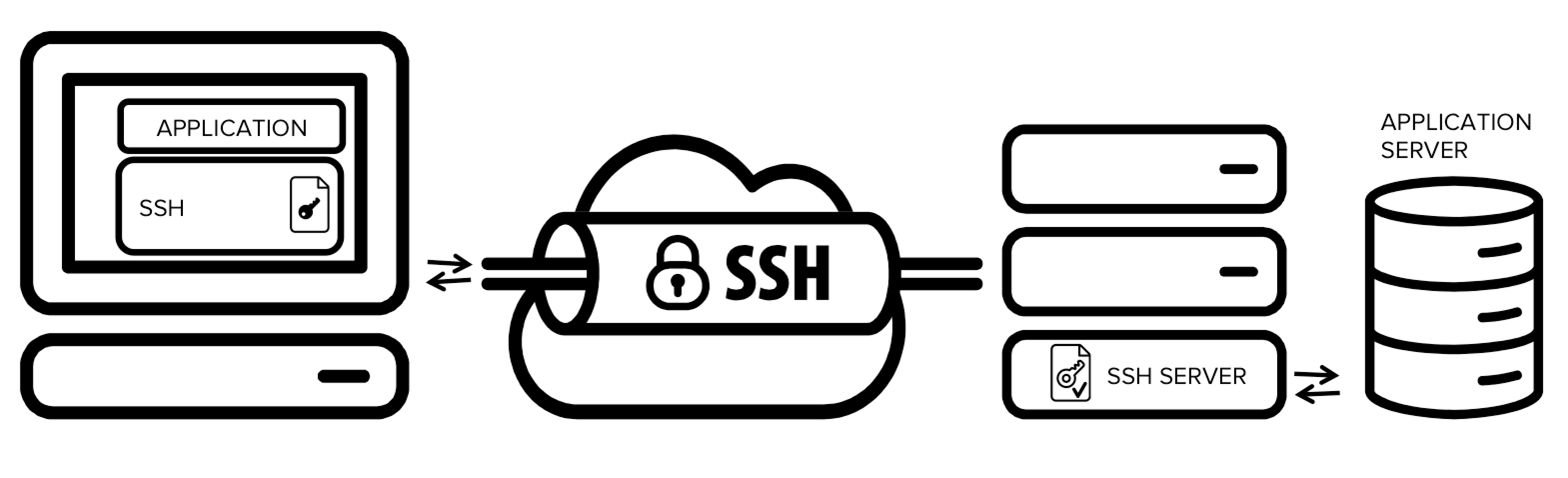
SSH uses port 22 to enable data encryption of payloads being transmitted over a public network (such as the Internet) connection, thereby providing VPN functionality. A tunnel is not encrypted by default: the TCP/IP protocol chosen determines the level of security. The Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) allows the transmission of frames between two nodes. It is also possible to establish a connection using the data link layer. In this case, the delivery and payload protocols are the same, but the payload addresses are incompatible with those of the delivery network. Technical overview Īs an example of network layer over network layer, Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE), a protocol running over IP ( IP protocol number 47), often serves to carry IP packets, with RFC 1918 private addresses, over the Internet using delivery packets with public IP addresses. The proxy allows connections only to specific ports, such as 443 for HTTPS. Because this creates a security hole, CONNECT-capable HTTP proxies commonly restrict access to the CONNECT method. The proxy then makes a TCP connection to a particular server:port, and relays data between that server:port and the client connection. A client issues the HTTP CONNECT command to a HTTP proxy. If the firewall policy does not specifically exclude this kind of "wrapping", this trick can function to get around the intended firewall policy (or any set of interlocked firewall policies).Īnother HTTP-based tunneling method uses the HTTP CONNECT method/command. Users can also use tunneling to "sneak through" a firewall, using a protocol that the firewall would normally block, but "wrapped" inside a protocol that the firewall does not block, such as HTTP. The chkconfig command prevents the Reverse SSH service from starting after a reboot.A tunneling protocol may, for example, allow a foreign protocol to run over a network that does not support that particular protocol, such as running IPv6 over IPv4.Īnother important use is to provide services that are impractical or unsafe to be offered using only the underlying network services, such as providing a corporate network address to a remote user whose physical network address is not part of the corporate network. The service command turns off the Reverse SSH service. Stopped Uplogix ~]# chkconfig matchmaker off
Shutting down Uplogix MatchMaker: Waiting for Uplogix MatchMaker to exit.
#Ssh tunnel app password
password for ~]# service matchmaker stop If you will not be using Reverse SSH and would like to close port 2222, you can do so by becoming root and issuing the following commands: ~]$ sudo su. Local: 198.51.100.48:36169 (47:53) Disabling Reverse SSH Tunnelsīy default, the Control Center will listen for Reverse SSH connections on port 2222. To view the status of the Reverse SSH tunnel, log into the Local Manager and run the show system reverse-ssh command. The Applet will automatically connect to the Reverse SSH proxy on the Control Center, which will then connect the Applet to the Local Manager via the Reverse SSH tunnel. This feature is separate from the SS5 SOCKS proxy and does not require it to be present or configured.Ĭlick on the SSH button on the Local Manager Summary page to initiate a connection.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
